The coding industry is experiencing rapid changes with the AI coding tools, ranging from basic code completion to full-scale software development lifecycle.
Let's borrow the terminologies from autonomous self-driving cars to categorize these tools into five levels: L1 to L5.
| Level | High-level Approaches | Example Popular Products |
|---|---|---|
| L1 | Code-level Completion | GitHub Copilot, Tabby |
| L2 | Task-level Code Generation Ticket to Code IDE with Chat | ChatGPT, Claude aider, cline, 16x Prompt Cursor, Continue, PearAI, Windsurf |
| L3 | Project-level Generation Ticket to PR Prompt to UI | Claude Code, Codegen, Sweep Pythagora, Plandex v0 |
| L4 | PRD to Production AI Software Engineer | bolt.new, Trickle, Lovable Devin, Genie, Engine, devlo, Gru |
| L5 | AI Development Teams | AutoDev, MetaGPT, MGX |
2D quadrant visualization of AI coding landscape as of June 2025 (view live version):
Code Completion (L1)
At the foundational level, L1 tools like GitHub Copilot focus on code completion.
GitHub Copilot excels at code completion
These tools are useful for developers, streamlining the coding process with intelligent suggestions and completions.
They have become the norm in modern development environments nowadays, paving the way for more advanced AI coding tools.
Code Completion (L1) Products
Paid:
Open-source:
Task-Level Automation (L2)
L2 focuses on task-level automation.
We have LLMs like ChatGPT. They are good at handling development tasks such as new features, bug fixes, and refactoring based on descriptive prompts.
ChatGPT is a versatile LLM model that can assist with coding tasks
However, using LLMs for coding tasks can be challenging. We need well-crafted prompts and relevant source code context to generate good quality code. Manually creating these prompts can be time-consuming and tedious.
To address these issues, we have workflow automation tools such as aider (command line tool) and 16x Prompt (desktop application), which aims to streamline the process of generating prompts and getting the best quality code from LLMs.
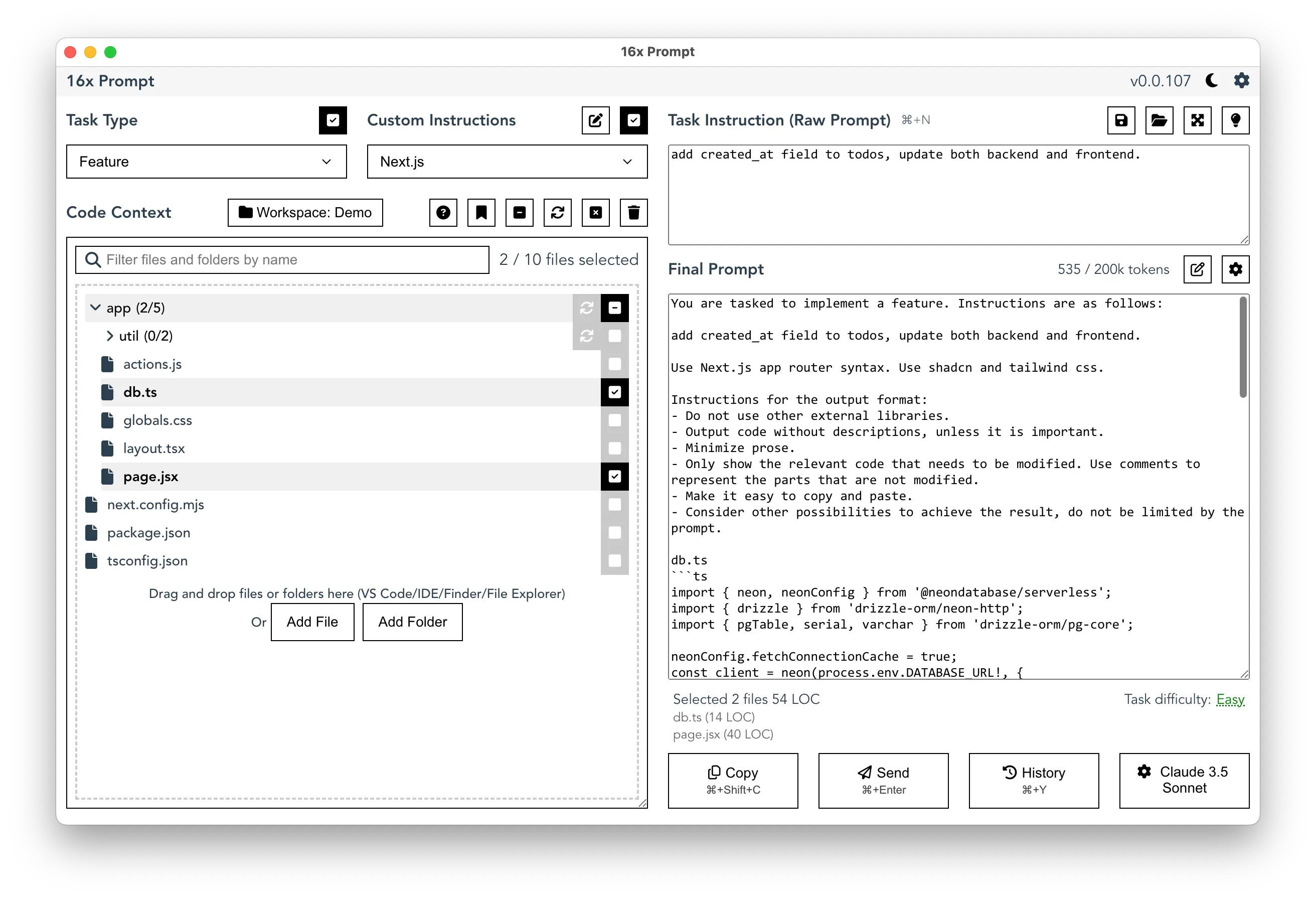
We also have IDEs and IDE extensions like Cursor, Continue, and PearAI that integrate LLMs into the development environment, providing a seamless experience for developers.
These tools are starting to enter the market, providing a more user-friendly interface for developers to interact with LLMs and automate coding tasks.
Task-Level Automation (L2) Products
LLMs:
Workflow Automation Tools:
- aider (Command line tool)
- 16x Prompt (Desktop application)
IDE Extensions:
IDEs:
- Replit CDE (Cloud development environment)
- Cursor
- PearAI
- Windsurf
- Trae
Project-Level Automation (L3)
L3 represents an early stage in project-level automation. Tools such as Claude Code, OpenAI Codex, Google Jules demonstrate abilities to take a project, analyze its requirements, and generate relevant pull requests.
OpenAI Codex demonstrates end-to-end automation from task to PR
A key feature of these L3 tools is the ability to automate multiple steps of the software development process, such as requirement gathering, code generation, pull request creation and deployment. This is achieved by integrating with project management tools like Jira and source code platforms like GitHub.
However, these systems are at a preliminary stage, capable of managing relatively simple coding projects and generating basic code snippets. They require human intervention to ensure code quality and relevance, limiting their autonomy.
Some tools like v0 by Vercel, Tempo by Tempo Labs and CerebrasCoder allows you generate websites from end-to-end. However, they typically only deal with one part of the software tech stack only, such as frontend.
Project-Level Automation (L3) Products
Tools from First-party Model Providers:
- Claude Code by Anthropic
- Codex by OpenAI
- Jules by Google
Paid:
Free:
- CerebrasCoder
- LlamaCoder
- AppCrapper (Requires API key)
Partially Open-source:
AI Software Engineer (L4)
L4 marks the key transition from human-driven coding to AI-driven software development. Development processes are fully automated, from product requirements to production deployment.
At this level, we have tools like Devin, Marblism and Genie from Cosine.
They envisioned to have access to terminals and deployment tools, capable of managing the entire spectrum of development activities.
Sample projects made with Marblism
SWE-bench Verified Leaderboard (as of Dec 19, 2024)
These advanced systems can interpret product requirements, manage code deployment, and maintain software in production environments, embodying the role of an AI software engineer. They enable non-technical people to go from zero to a fully functional software product in minutes.
AI Software Engineer (L4) Products
Focused on Full-stack Web Development:
Launched, Publicly Available:
- devlo - 54.20 on SWE-bench Verified (2024-11-08)
- Gru - 45.20 on SWE-bench Verified (2024-08-24)
- Devin - $500 USD for 250 Agent Compute Units (ACUs) volume-based pricing
Read my first impressions review of Devin here
Launched, Contact Sales / Onboard Required:
- Engine - 51.80 on SWE-bench Verified (2024-11-25)
- Factory Code Droid - 19.27 on SWE-bench Full (2024-06-17)
Upcoming / Waiting List / Request Early Access:
- Solver - 50.00 on SWE-bench Verified (2024-10-28)
- Genie - World's best AI Software Engineer
- Tessl - AI Native development platform
AI Development Teams (L5)
At L5, AI coding will most likely involve an AI system with multiple AI Software Engineer as described above. These AI agents can collaborate and work together on a project, each specializing in different aspects of software development.
For example, in the Microsoft paper AutoDev, it was proposed that agents can "receive objectives and conversation histories from the Agent Scheduler, responding with actions specified by the Rules and Actions configuration".
However, only "a single GPT-4 agent" was used for evaluation in the paper.
AutoDev enables an AI Agent to achieve a given objective by performing several actions within the repository. Source: https://arxiv.org/html/2403.08299v1
Another product in this category is MGX. It is designed by the MetaGPT team and is currently in waiting list.
MGX by the MetaGPT team landing page
With the GPT-5 expected to release in 2025, the dream of AI development teams is not far-fetched.
We could see a future where the AI system could replicate entire software development teams, coding and collaborating across different facets of software creation.
AI Development Teams (L5) Products
Research:
Open-source:
Commercial Waiting List:
Commercial Contact Sales:
Which Level is Right for You?
The choice of AI coding tools depends on your needs and the complexity of your projects.
If you just need help with code completion, L1 tools like GitHub Copilot are sufficient.
For more complex tasks like feature development and bug fixes, L2 LLMs like ChatGPT or Claude 3 can be used together with workflow automation tools like aider or 16x Prompt.
If you are adventurous and want to experiment with project-level automation, L3 tools like Codegen or Sweep can be a good starting point.
Also, you don't have to stick to one level. You can use a combination of tools from different levels to suit your specific requirements.
For example, I use GitHub Copilot for simple code completion tasks that can be solve in 5 seconds, ChatGPT and 16x Prompt for more complex tasks that require a few minutes of prompting.
Looking Ahead
In 2025, AI's role in coding is rapidly evolving, from basic syntax assistance to full-scale development lifecycle management.
As AI continues to mature, we can expect more sophisticated tools that will redefine the coding landscape, enabling developers to focus on higher-level tasks while AI handles the routine aspects of software development.